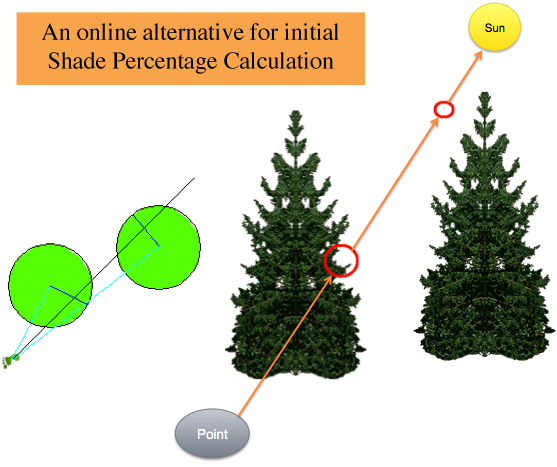

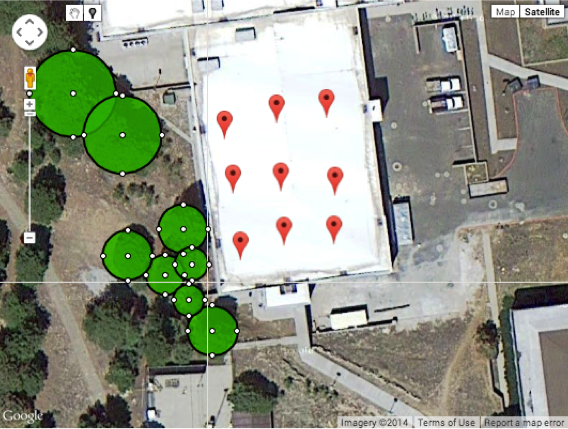
This tool will allow the user to perform shade analysis through a satellite image from Google Maps®. The image is retreived through entering an address and the locations and heights of the solar panels, along with the obstructions around the building, are marked using visual tools. This information is then run through an algorithm to output the percentage of shade that will hit those panels over the course of a year. This was created with the knowledge of the inefficiencies in the solar industry; this application allows companies to provide an initial shade estimate without sending employees onto the roof of every potential client's building.
Solar calculation in the past has always been done using devices such as a SunEye to get an estimate
on how much sunlight would hit their building over the course of a year for a client.
In contrast, this application changes that idea. Instead of going on-site and taking a photo upward
using a SunEye device, this will use Google Maps and use a top-down approach to estimate the shade percentage.
The client must give estimates of the heights of surrounding obstructions, such as trees or surrounding buildings,
where this information can be put into the application. The application can then simulate the sun at different
times of the day and throughout the course of a year. After, it will output a shade percentage within
2-3% accuracy of the result from the SunEye device. This will allow for a quick response to the client with an
initial shade estimate, potentially leading to a quicker contract, in less time, and less resources wasted.
